-
 WHATSAPP
WHATSAPP -
 INS
INS -
 WECHAT
WECHAT
The Evolution and Impact of CNC Lathe Machines
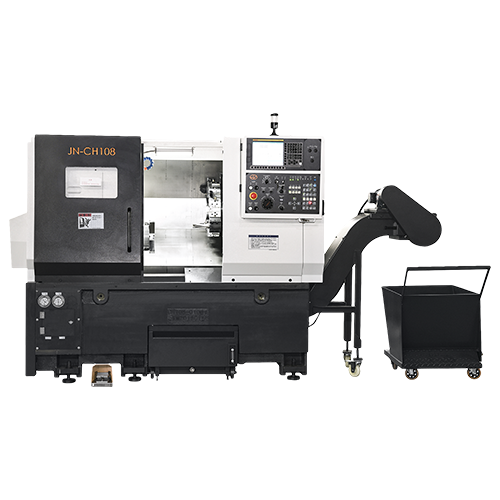
Wholesale CNC Lathe Turning Machine Supplier Manufacturer
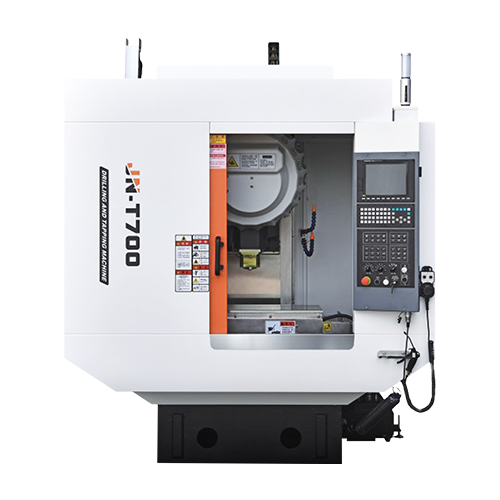
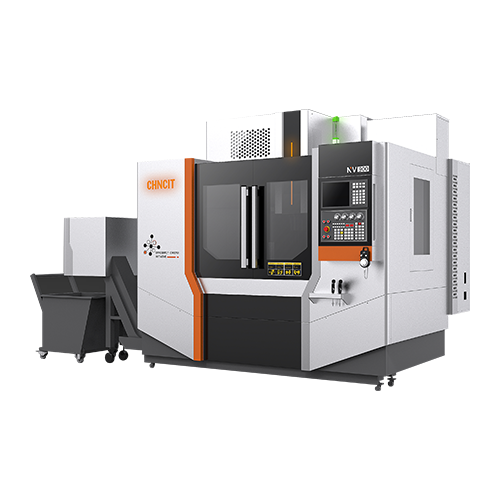
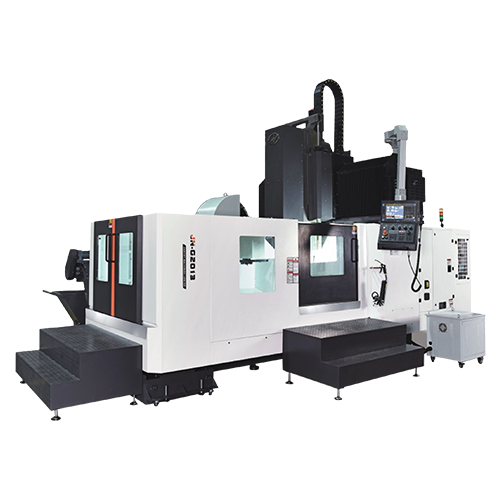
CNC Lathe Machines are advanced manufacturing tools that use computer programming to control the movement of cutting tools against a rotating workpiece. They are designed for precision machining of cylindrical parts and can perform various operations such as turning, drilling, and threading. These machines offer high accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency, making them essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment manufacturing.
The lathe, in its basic form, has been a staple in workshops for centuries. However, the advent of computer technology in the 20th century paved the way for the development of CNC lathes. These machines combine the precision of a traditional lathe with the versatility and speed of computer-aided design and manufacturing.
The first CNC lathes were introduced in the 1950s, and since then, they have undergone significant advancements. Early models were limited in their programming capabilities, but as computer technology advanced, so did the complexity and precision of CNC lathes. Today, they are equipped with sophisticated software that allows for intricate designs and complex machining operations.
CNC lathes are designed to perform a variety of tasks with high precision. Some of their key features include:
Automation: Once a program is loaded, the machine can operate autonomously, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing productivity.
Versatility: They can handle a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics, and are capable of producing both simple and complex parts.
Precision: The use of computer-controlled systems ensures that each part is produced to exact specifications, reducing waste and improving quality.
Repeatability: CNC lathes can produce identical parts with minimal variation, which is crucial for industries that require standardized components.
The integration of CNC lathes into manufacturing processes has had a profound impact:
Increased Productivity: Automation allows for longer production runs with less downtime, leading to higher output and efficiency.
Reduced Labor Costs: By minimizing the need for skilled labor, companies can reduce their operational costs.
Enhanced Quality Control: The precision of CNC lathes leads to fewer defects and a higher quality of finished products.
Customization: The ability to quickly change programs allows for the production of customized parts, catering to the needs of niche markets.
CNC lathes are not limited to a single industry; they are used across a spectrum of sectors, including:
Automotive: For the production of engine components, transmission parts, and other precision components.
Aerospace: In the manufacturing of aircraft components that require high precision and strength.
Medical: For the production of intricate medical devices and instruments.
Consumer Electronics: In the creation of small, precise parts for electronic devices.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will CNC lathes. Future developments may include:
Advanced Materials Handling: The ability to work with new materials as they are developed.
Improved Software: Enhanced programming capabilities to facilitate more complex designs.
Integration with Other Technologies: Such as robotics and 3D printing, to create a more seamless manufacturing process.
CNC lathe machines have come a long way since their inception, and their impact on the manufacturing industry is undeniable. They have transformed the way products are made, enabling greater precision, efficiency, and customization. As technology advances, the capabilities of CNC lathes will continue to expand, further shaping the future of manufacturing.